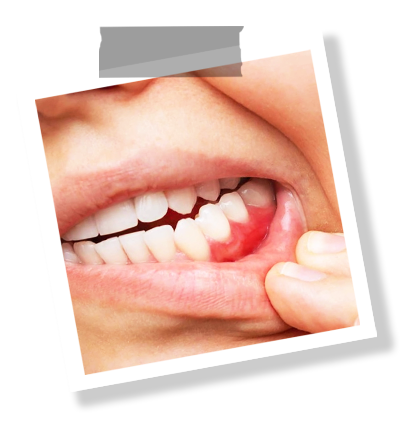
Gum Transplant (Gingival Graft)
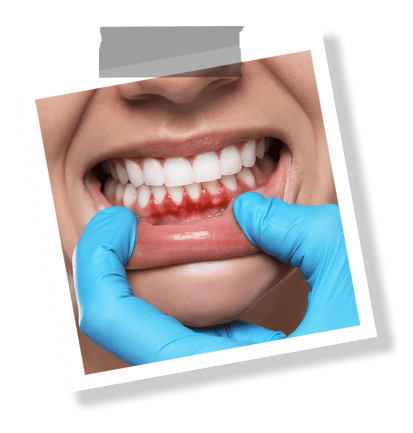
A gum transplant is an effective surgical treatment for advanced gum recession. Exposing the root surfaces of teeth can pose both aesthetic and health concerns. Over time, this can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss. A gum graft reconstructs the lost gum tissue, preserving the natural appearance and health of the tooth.
Contact Us